8 Powerful Scenarios for Training Teams Effectively in 2025
Traditional training methods often fall short. Reading a manual or watching a passive video doesn't prepare employees for the high-stakes, nuanced decisions they face daily. The gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application is where skills break down and costly mistakes happen. This is why forward-thinking organizations are moving beyond static content and embracing interactive video. By creating realistic scenarios for training, you immerse learners in dynamic situations, forcing them to make choices and experience the direct consequences of their actions in a safe, controlled environment.
This article moves beyond theory to provide a deep dive into practical, replicable examples. We will dissect eight distinct training scenarios, from crisis management simulations to complex sales negotiations. You won't find surface-level descriptions here. Instead, you'll get a strategic breakdown of each scenario, revealing the specific interactive features used, the psychological drivers at play, and the measurable outcomes achieved. To truly unlock the potential of interactive scenarios, it's essential to understand the underlying pedagogical approaches, such as comprehensive instructional design principles.
Our goal is to provide you with a blueprint. Each example includes actionable takeaways and tactical insights you can immediately apply to your own learning and development programs. Prepare to see how to transform passive viewers into active participants, improve knowledge retention, and build critical skills that translate directly to real-world performance.
1. Crisis Management Simulation
A crisis management simulation is one of the most powerful scenarios for training available, thrusting participants into a high-stakes, time-sensitive emergency to test their decision-making under pressure. Using interactive video, these simulations move beyond theoretical knowledge to replicate the stress and uncertainty of a real-world crisis, such as a sudden data breach, a workplace safety incident, or a PR disaster unfolding on social media.
The core of this method involves a branching narrative. A primary video presents the initial incident, forcing the learner to make a critical first choice. For example, after a simulated chemical spill, a manager might be asked: Do you A) immediately evacuate the entire floor or B) first attempt to contain the spill with the emergency kit? Each decision leads down a different path with unique consequences, challenges, and subsequent choices, creating a dynamic learning experience.
Strategic Analysis
The effectiveness of a crisis simulation lies in its ability to mimic real-world pressure. Time-limited choices, where a decision must be made within seconds, prevent over-analysis and reveal a learner’s true instincts. The interactive video can also introduce unexpected variables, like a news reporter calling for a comment or a key team member becoming unreachable, which further tests adaptability. This approach transforms passive learning into active problem-solving.
Strategic Insight: The goal isn't just to teach the right procedure but to let learners experience the consequences of wrong decisions in a safe environment. This failure-driven learning is profoundly more memorable than simply reading a crisis plan.
Actionable Takeaways
To implement this effectively, focus on realistic consequences and feedback.
- Design for Impact: Ensure each choice leads to a tangibly different outcome. If containing a spill fails, show a video of the situation worsening. If the evacuation is handled poorly, present a mock news report detailing the negative fallout.
- Integrate Data & Feedback: Use hotspots or clickable overlays on the video to provide supplementary information, like schematics or contact lists, mimicking real-world resources.
- Provide a Debrief: At the end of the simulation, provide a detailed summary of the user's path, highlighting critical decision points and explaining the ideal response based on company protocol. This links the simulated experience back to concrete organizational policy.
2. Customer Service Role-Playing
Customer service role-playing is one of the most effective scenarios for training because it directly prepares employees for real-world interactions. These scenarios use interactive video to place learners in the shoes of a service representative handling various customer situations, from simple inquiries to complex, emotionally charged complaints. This method is crucial for developing empathy, refining communication skills, and mastering problem-solving in high-pressure, customer-facing roles.

The simulation presents a video of a customer with a specific problem. For example, a retail associate might face an agitated customer whose online order was never delivered. The learner must then choose a response: A) Immediately offer a full refund and an apology or B) First ask for the order number to investigate the issue. Each choice triggers a different video response from the customer, simulating the natural flow of conversation and the impact of the employee's words and tone.
Strategic Analysis
The power of interactive role-playing lies in its ability to build emotional intelligence alongside procedural knowledge. Unlike static scripts, these scenarios allow employees to practice de-escalation and active listening in a controlled setting. The interactive video format can capture subtle nuances, like a customer's tone of voice or body language, that are impossible to convey in text. This forces learners to read social cues and adapt their strategy in real time.
Strategic Insight: The primary goal is not just to teach the company's service policy but to train the emotional agility needed to apply it effectively. Allowing learners to see a customer become more frustrated based on a poor choice is a more powerful lesson than any manual.
Actionable Takeaways
To maximize the impact of role-playing scenarios, focus on realism and constructive feedback loops.
- Build a Diverse Scenario Library: Create a wide range of situations based on real customer feedback. Include interactions with different personality types, such as calm, confused, angry, or appreciative customers, to prepare staff for any possibility.
- Incorporate Tone Matching: Use choices that reflect different tones, not just different actions. For instance, offer an empathetic option versus a purely transactional one, and show how the customer's video response changes accordingly.
- Provide Contextual Feedback: After a path concludes, use on-screen text or a "mentor" video to explain why a certain approach was more effective. Highlight specific communication techniques, like reflective listening or positive phrasing, that led to a successful outcome.
3. Leadership Decision-Making Scenarios
Leadership decision-making scenarios are sophisticated scenarios for training designed to test and develop a leader's strategic judgment. Far from simple right-or-wrong questions, these simulations present leaders with complex business problems characterized by competing priorities, ethical gray areas, and incomplete information. Drawing inspiration from Harvard Business School case studies and GE's famous leadership programs, they force participants to weigh long-term strategic goals against immediate operational needs.
The scenario unfolds through interactive video, placing the learner in the role of a senior leader facing a critical challenge. For example, a leader might be presented with a promising but costly innovation project while the company faces pressure to cut costs. They must decide: Do they A) allocate scarce resources to the long-term, high-risk project or B) prioritize short-term profitability by deferring the investment? Each choice triggers a new set of consequences, such as stakeholder reactions, team morale shifts, or competitive market movements.
Strategic Analysis
The power of this method lies in its realism and focus on the decision-making process. It's not about finding a single correct answer but about teaching leaders how to navigate ambiguity, manage stakeholder interests, and justify their strategic choices. The scenarios are often layered with ethical dilemmas, such as balancing shareholder returns with employee welfare, forcing leaders to apply their values under pressure. This moves training beyond procedural knowledge into the realm of strategic wisdom.
Strategic Insight: These scenarios excel at revealing a leader's cognitive biases and default decision-making patterns. By allowing them to see the multi-stage fallout of a single choice in a controlled setting, the training provides a powerful mirror for self-reflection and growth.
Actionable Takeaways
To build effective leadership simulations, ground the experience in authentic, high-stakes trade-offs.
- Base on Real Cases: Adapt real-world business challenges, anonymized if necessary, to create scenarios with authentic complexity and pressure. This ensures the dilemmas feel relevant and weighty.
- Focus on Process Over Outcome: Use feedback to analyze the why behind a leader's choice. Prompt them to articulate their reasoning at key decision points, then provide expert commentary on their thought process.
- Incorporate Group Deliberation: Structure the scenario for teams. Have individuals make an initial choice, then present them with a video of peers arguing for an alternative path, forcing them to defend or reconsider their position.
This infographic visualizes the fundamental trade-off between urgent needs and strategic goals, filtered through the critical lens of resource availability.
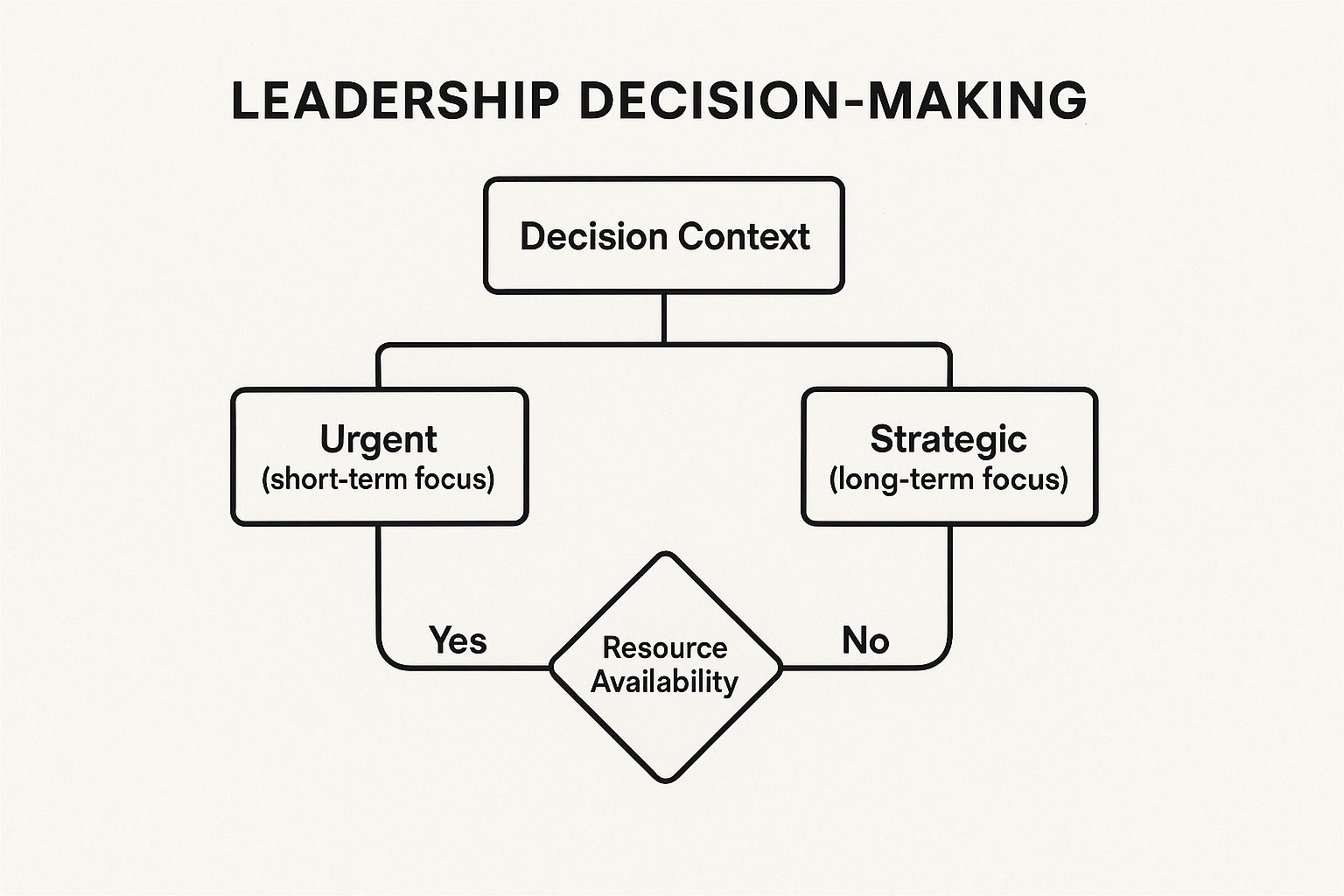
The decision tree highlights how resource constraints fundamentally alter the viability of both short-term and long-term actions, forcing leaders to make pragmatic choices. You can learn more about scenario based training on mindstamp.com to explore these concepts further.
4. Sales Negotiation Simulations
Sales negotiation simulations are highly effective scenarios for training that immerse sales professionals in realistic, high-stakes customer interactions. These simulations go beyond standard role-playing by using interactive video to replicate the nuances of a complex sales cycle. Participants practice objection handling, value proposition delivery, and relationship building in a controlled environment, facing scenarios inspired by methodologies like SPIN Selling or the Challenger Sale.
The simulation typically begins with a video introducing a prospective client and their business challenge. The learner must then navigate a series of dialogue choices to uncover needs, present solutions, and negotiate terms. For instance, after a client expresses a budget concern, the salesperson might be prompted to choose between: A) offering an immediate discount or B) reframing the conversation around long-term ROI. Each choice triggers a different video response from the client, realistically escalating or de-escalating the negotiation.
Strategic Analysis
The power of a sales negotiation simulation is its ability to model the psychological and emotional dynamics of a real sales conversation. By using video of actors portraying different customer personas, from the analytical CFO to the skeptical IT manager, the training captures non-verbal cues and emotional shifts. This forces learners to adapt their strategy in real-time, moving beyond scripted responses to develop genuine conversational agility and empathy.
Strategic Insight: These simulations are not about memorizing the perfect pitch. They are designed to build a salesperson's "muscle memory" for handling difficult conversations, allowing them to practice poise and strategic thinking when faced with real-world pressure.
Actionable Takeaways
To create a compelling sales simulation, concentrate on authenticity and targeted feedback.
- Build Realistic Personas: Use actual customer data and sales team anecdotes to create client personas. Script their objections and questions based on real-life challenges your team frequently encounters.
- Incorporate Competitive Pressure: Introduce variables like a competitor’s offer or a sudden change in the client’s internal priorities. Use on-screen notifications or timed events to simulate these unexpected hurdles.
- Provide Path-Specific Feedback: After the simulation, offer a playback of the user's conversation. Use annotations to highlight key decision points, explain why a particular response was effective or not, and link the ideal choices back to your organization’s specific sales methodology.
5. Medical Emergency Simulations
Medical emergency simulations are among the most critical scenarios for training, utilizing high-fidelity mannequins and standardized patient actors to replicate life-or-death situations. These exercises, often conducted in dedicated centers like those at Johns Hopkins or the Mayo Clinic, go beyond theory to test clinical skills, teamwork, and communication under immense pressure. Using interactive video to record and debrief these sessions enhances learning by allowing teams to analyze their performance in detail.
The simulation often begins with a video brief outlining a patient's symptoms, followed by the hands-on scenario in a realistic setting. For instance, a team might face a mannequin simulating a cardiac arrest. They must correctly perform CPR, administer medications, and use a defibrillator. An interactive overlay on the debrief video could then ask: A) Was the first dose of epinephrine administered within the recommended 3-5 minute window? or B) Did the team leader provide clear, closed-loop communication during resuscitation?
Strategic Analysis
The power of these simulations lies in their realism and the integration of both technical and soft skills. Unlike purely academic exercises, these scenarios introduce unpredictable human factors, such as a panicked family member (played by an actor) or an equipment malfunction, forcing participants to adapt dynamically. While focusing on real-world simulations, it's also important to consider how medical professionals prepare for high-stakes assessments, where strategic use of practice exams can simulate the testing environment and challenge clinical decision-making. Developing strong strategies for NBME practice exams is a complementary skill set that sharpens the diagnostic reasoning tested in these simulations.
Strategic Insight: The primary goal is to close the gap between knowing what to do and being able to do it effectively as a team in a chaotic environment. The debrief, facilitated by video playback, is where the most profound learning occurs.
Actionable Takeaways
To maximize the impact of medical simulations, focus on comprehensive, data-driven debriefing.
- Integrate Performance Metrics: During the video debrief, use on-screen timers and annotations to highlight critical moments, like the time-to-defibrillation or delays in medication administration, providing objective performance data.
- Capture Communication Nuances: Focus the camera on team interactions, not just the patient. Use the video to analyze communication breakdowns, body language, and leadership effectiveness, which are often missed in the moment.
- Run Escalating Scenarios: Design simulations that increase in complexity. Start with a common emergency and progress to a rare, multi-layered crisis that incorporates fatigue factors or resource limitations to build resilience.
6. Cybersecurity Incident Response Training
Cybersecurity incident response training uses highly technical scenarios for training that simulate real-world cyberattacks, forcing IT and security teams to execute detection, containment, and recovery protocols under immense pressure. These simulations go far beyond multiple-choice quizzes, often using interactive video to present unfolding attack vectors like a phishing campaign leading to a ransomware outbreak or a sudden data breach discovery. Participants must navigate the scenario using simulated tools and communication channels.
The simulation starts with an initial alert, presented via an interactive video or a dashboard. For instance, an analyst sees a notification about unusual outbound network traffic. They must then decide how to investigate: A) Immediately block the suspicious IP address or B) Analyze the traffic patterns to identify the source and scope first? Each decision triggers a new video segment, showing the consequences of their action, such as the attacker changing tactics or critical systems going offline, creating a high-fidelity learning environment.
Strategic Analysis
The power of these simulations comes from mirroring the technical complexity and communication challenges of an actual security incident. Timed events and branching paths force participants to prioritize actions, manage resources, and communicate with non-technical stakeholders, like legal or executive teams. The scenario can introduce injects such as a mock press inquiry or a regulatory compliance notification, testing both the technical response and the business-level handling of the crisis.
Strategic Insight: The primary goal is not just to test technical skills but to build muscle memory for the entire incident response lifecycle. Letting a team "fail" to contain a simulated breach in a safe setting reveals gaps in their process, communication, and tooling before a real attack occurs.
Actionable Takeaways
To create effective cybersecurity simulations, focus on realism and integrated feedback loops.
- Base Scenarios on Threat Intel: Design scenarios using real-world attack chains from recent threat intelligence reports, such as those from Mandiant or CrowdStrike. This ensures the training is relevant and prepares teams for current adversary tactics.
- Integrate Legal and Compliance: Use interactive elements to force decisions with legal ramifications. For example, a pop-up asks if the team should notify regulatory bodies now or after a full investigation, with each choice having distinct legal and reputational outcomes.
- Practice Executive Communication: Include branching paths where participants must create a summary report for a non-technical executive. The video can then show a simulated CEO reacting positively or negatively to the clarity and business impact described in the update.
7. Team Collaboration and Conflict Resolution
Team collaboration and conflict resolution simulations are among the most nuanced scenarios for training, designed to improve interpersonal dynamics and communication. These scenarios use interactive video to place learners in realistically awkward or tense workplace situations, forcing them to navigate difficult conversations, manage competing priorities, and resolve disputes among colleagues. The goal is to build emotional intelligence and collaborative problem-solving skills in a controlled setting.
The training typically begins with a video depicting a common team-based challenge, such as a project meeting where two key members have a heated disagreement over strategy. The learner, playing the role of a team lead or a neutral colleague, must then choose how to intervene. For instance, do they A) address the conflict publicly to get immediate alignment or B) suggest a private follow-up conversation with the individuals involved? Each choice triggers a different set of reactions and consequences, illustrating the ripple effects of their communication style.
Strategic Analysis
The power of these simulations comes from their focus on "soft skills," which are notoriously difficult to teach through traditional methods. By simulating interpersonal friction, the training forces learners to practice active listening, empathy, and de-escalation tactics in a context that feels real. The branching video can dynamically represent body language and tone shifts in response to a learner’s choices, providing immediate, non-verbal feedback that a textbook cannot.
Strategic Insight: The primary objective is not to teach a single "correct" way to resolve conflict but to build a versatile toolkit of communication strategies. The simulation should demonstrate that different approaches may be required for different personalities and situations, promoting adaptability over rigid procedural adherence.
Actionable Takeaways
To create effective collaboration scenarios, focus on psychological safety and realistic dialogue.
- Model Realistic Conflicts: Base scenarios on actual, anonymized conflicts from within the organization. This ensures the challenges are relevant and resonate with employees, whether it's a dispute over resource allocation or a clash of working styles.
- Emphasize Empathy Building: Use interactive elements to let the learner see the situation from multiple perspectives. After a choice is made, an optional video could show how another team member perceived their intervention, building awareness of impact. You can explore how interactive video can enhance these training exercises by checking out some examples of interactive online training.
- Debrief on Principles, Not Just Actions: The feedback session should connect the learner’s choices to core conflict resolution principles, like focusing on shared interests rather than fixed positions. Provide specific language and framing techniques they can apply in their next real-world team interaction.
8. Safety Protocol and Emergency Evacuation Drills
Safety protocol and emergency evacuation drills are critical scenarios for training that move beyond theoretical knowledge into practical, life-saving application. These interactive simulations immerse learners in urgent situations like a fire, chemical spill, or sudden equipment failure, compelling them to react correctly under pressure. Instead of just reading a manual, participants are placed in a first-person perspective video of an escalating emergency.
The simulation starts with an inciting incident, such as an alarm sounding or visible smoke. The learner must then make a sequence of choices based on established safety protocols. For instance, in a simulated lab fire, the user might have to decide: Do you A) locate and use the nearest fire extinguisher or B) immediately trigger the main alarm and evacuate? Each decision leads to a different video outcome, showing the direct consequences of their actions and reinforcing the correct procedure.
Strategic Analysis
The power of these drills lies in building muscle memory for emergency procedures. By using interactive video, organizations like DuPont have digitized their legendary safety methodologies, making complex response training scalable and consistent. The simulation can test not just the primary action but also secondary considerations, such as assisting a colleague with mobility issues or remembering the designated outdoor muster point, all through choice-based video paths.
Strategic Insight: The key is to simulate the sensory overload of a real emergency. Flashing lights, loud alarms, and time-sensitive choices in the video prevent rote memorization and force genuine, instinctual application of safety training in a controlled, risk-free setting.
Actionable Takeaways
To execute these drills effectively, focus on realism and post-simulation reinforcement.
- Vary the Scenarios: Create multiple drill variations to prevent predictability. Simulate emergencies during different times of the day or under challenging conditions, such as a power outage, to test adaptability.
- Integrate Equipment Checks: Use clickable hotspots on emergency equipment shown in the video, like an eyewash station or fire extinguisher. This can trigger a pop-up quiz about its proper use or inspection date, blending procedural knowledge with equipment readiness.
- Debrief for Improvement: Conclude every simulation with a clear, non-punitive debrief. Provide a summary of the learner's choices against the optimal path defined by OSHA or NFPA standards. This is where true learning happens, connecting the simulated experience to real-world safety compliance. For more ideas, you can explore detailed examples of branching safety training on mindstamp.com.
Training Scenario Types Comparison
Start Building Your High-Impact Training Today
Moving beyond passive learning is no longer a luxury; it's a strategic necessity for impactful training and development. As we've explored through a diverse range of examples, from high-stakes crisis management to nuanced sales negotiations, the power of interactive video lies in its ability to create immersive, memorable, and measurable learning experiences. The common thread connecting all these powerful scenarios for training is the shift from simply telling learners what to do to letting them experience the consequences of their choices in a safe, controlled environment.
This active participation is where true learning flourishes. By building these scenarios, you're not just creating content; you're crafting dynamic practice fields where employees can hone critical skills, build confidence, and align their actions with organizational goals. The detailed breakdowns of each scenario demonstrate that this approach is far from a one-size-fits-all solution. Instead, it is a highly adaptable framework that can be tailored to meet specific, critical business needs.
Your Path from Theory to Application
The journey from understanding these concepts to implementing them is straightforward. The key is to start with a clear objective and work backward.
- Identify the Core Skill: What specific competency, from de-escalating customer complaints to responding to a cybersecurity threat, do you need to improve?
- Map the Decision Points: What are the critical choices an employee must make in this situation? These become the interactive branching points in your video.
- Define Success and Failure: What does a successful outcome look like? What are the common mistakes or pitfalls? Use these to build out your feedback loops and learning paths.
- Leverage Data for Iteration: Use analytics from your interactive videos to see where learners struggle. This data is invaluable for refining your training scenarios for training and identifying broader knowledge gaps within your teams.
Strategic Takeaway: The most effective training scenarios are not just about testing knowledge, but about shaping behavior. By simulating real-world pressures and outcomes, you provide a powerful context that makes learning stick, driving tangible improvements in performance, safety, and decision-making across your organization.
Ultimately, mastering the art of creating compelling scenarios for training empowers you to close the gap between knowing and doing. It transforms training from a passive, check-the-box activity into an engaging, data-driven engine for growth and operational excellence. The tools and strategies are at your fingertips; the opportunity now is to build the experiences that will define the future of learning in your organization.
Ready to transform your static videos into powerful, interactive training tools? Mindstamp makes it easy to build the immersive and data-rich scenarios for training discussed in this article. Start creating your own high-impact learning experiences today by exploring what you can build with Mindstamp.
Get Started Now
Mindstamp is easy to use, incredibly capable, and supported by an amazing team. Join us!


Try Mindstamp Free










