Applying Multimedia Learning Principles in Corporate Training
Multimedia learning principles are a set of research-backed guidelines for creating corporate training content that actually improves employee performance. They show you how to combine words, audio, and visuals in a way that aligns with how the human brain naturally learns, rather than fighting against it.
The goal? To boost both understanding and long-term knowledge retention for your workforce.
Why Your Corporate Training Isn't Sticking
Ever poured your budget into a new employee training video, only to find out a week later that your team barely remembers the key procedures? It's a frustratingly common problem in corporate development. You've also probably been on the receiving end—stuck in a compliance training so overloaded with text, animations, and a robotic narrator that you just tuned out.
This gap between delivering content and creating real understanding is where most corporate training fails. The issue usually isn't the information itself, but how it's presented. This is exactly where multimedia learning principles come in. They’re the blueprint for designing employee training that actually sticks.
Think of it like cooking. A beginner might just throw a bunch of good ingredients into a pan and hope for the best. But a chef understands how heat, timing, and flavors work together to create something amazing. The same goes for training. Tossing words, images, and audio together isn't enough; you have to combine them thoughtfully to create effective learning experiences for your team.
The Shift from Tech-First to Learner-First
In the early days of e-learning, companies got excited about the flashy new technology. The focus was all on what the tech could do, not on how employees actually learn. This led to a lot of overwhelming, tech-first content that looked impressive but failed to build skills.
Thankfully, there’s been a major shift. We've moved toward a learner-centered approach that puts the human brain first. Instead of asking, "What cool features can we add?", the smart question for any training manager is, "What does my employee's brain need to absorb this?"
The answer almost always involves reducing cognitive load—that’s the mental effort an employee has to put in just to process the training you're giving them. When training is confusing or overwhelming, the brain wastes all its energy trying to figure out the presentation itself, leaving no room to learn the actual content.
Building Training That Actually Works
When you apply these principles, you create a clear, simple path for information to travel from the screen into your employees' long-term memory. This isn't just an academic exercise; it has a direct impact on your business.
Here’s why this approach is so critical for your corporate training programs:
- Boosts Engagement: Content that is simple to process keeps employees focused. They're far less likely to get distracted or start multitasking during mandatory training.
- Improves Knowledge Retention: Using narration with relevant visuals, for instance, helps cement complex procedures and compliance rules in memory. You can learn more about this in our guide to effective knowledge retention strategies.
- Increases Training ROI: Better training leads directly to better job performance, fewer mistakes, and a more confident workforce. That's a real return on your investment.
The core idea is simple but incredibly powerful: Don't make the brain work harder than it has to. By aligning your training design with how people actually learn, you ensure your message isn't just seen, but truly understood and remembered.
Using an interactive video platform like Mindstamp is the perfect way to put these principles into practice. You can turn passive training videos into active learning experiences that build real skills and deliver measurable results for your organization.
How to Reduce Mental Clutter in Training Videos
We’ve all been there. You’re trying to watch a mandatory training video, but you’re completely overwhelmed. There’s distracting music, flashy graphics that don't add anything, and walls of text scrolling by. It’s too much for anyone to absorb.
The human brain can only process so much new information at once. When a training video is cluttered, it overloads that capacity. That's why several of the most important multimedia learning principles are all about one thing: reducing extraneous cognitive load.
Think of yourself as a guide clearing a path in a dense forest. Your job is to make it incredibly easy for the employee to walk from "I don't know" to "I get it" without tripping over a bunch of irrelevant details. By cutting out everything that doesn't directly help them learn, you free up their mental energy to focus on what actually matters.
Let's break down four essential principles that will help you cut through the noise and make your corporate training videos more direct, digestible, and effective.
The Coherence Principle
What It Means: Simply put, people learn better when you get rid of all the extra fluff. Extraneous words, pictures, and sounds are distractions, not enhancements. Less is almost always more in a professional learning context.
It sounds obvious, but it’s a trap we all fall into. That catchy background song? The cool-looking but irrelevant stock photo? That extra paragraph of "interesting trivia" about the company's history? They all get in the way of actual learning.
How to Apply It in Mindstamp:
- Audit Your Audio: Fight the urge to add background music to a process or compliance video. For focused learning, a clean, crisp voiceover is your best friend.
- Simplify Your Visuals: Every graphic and image should directly illustrate the point you’re making. If you're showing an employee how to use a software feature, zoom in on that specific feature, not the entire busy interface.
- Be Ruthless With Your Script: Go through your script with a red pen. Cut out the fun facts, the long-winded stories, and the jargon that doesn't directly support the main learning goal of the training module.
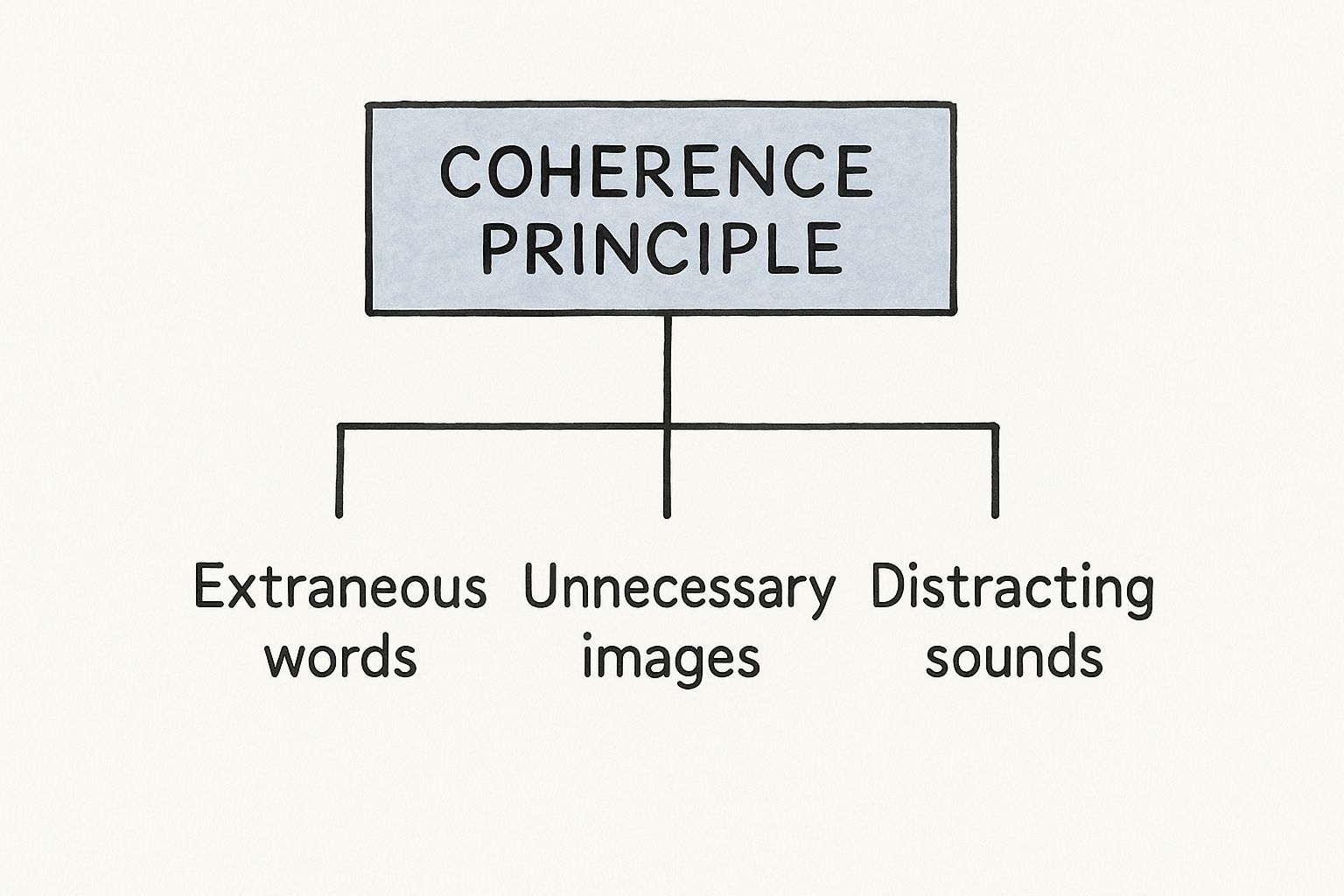
As you can see, the core idea is to eliminate these three sources of clutter. Doing so creates a learning experience that is focused and powerful.
The Signaling Principle
What It Means: People learn better when you add cues that highlight what's important. Signaling is like giving your employees a map and a highlighter for their training journey. You’re pointing directly at the key information.
Without these signals, employees waste precious mental energy just trying to figure out what they should be paying attention to. A simple visual nudge can make all the difference.
How to Apply It in Mindstamp:
- Use Hotspots and Highlights: Guiding someone through a software tutorial? Use Mindstamp's hotspot feature to draw a bright circle or box around the exact button they need to click. It’s impossible to miss.
- Add Text Callouts: A quick text overlay that says "Step 1" or "Key Takeaway" is a powerful way to direct the employee's focus at just the right moment.
- Leverage Chaptering: Break your training video into logical sections with Mindstamp’s chapter markers. This gives employees a clear roadmap of the content and lets them easily navigate to what they need.
By using signals, you're not just throwing information at someone; you're actively guiding their focus. This simple act of pointing things out makes a massive difference in how well they'll understand and remember the material.
The Redundancy Principle
What It Means: Here's a surprising one: people learn better from graphics and narration alone than from graphics, narration, and identical on-screen text. When you say the exact same words that are written on the screen, the brain gets confused.
It's forced to process the same information twice, creating a traffic jam in the brain’s visual channel as it tries to read the text and look at the image simultaneously. It's much cleaner to let the ears handle the words (narration) and the eyes handle the pictures (graphics).
How to Apply It in Mindstamp:
- Avoid Verbatim Subtitles: Instead of putting your entire script on the screen, use text overlays for only the most important keywords or short summary points. Let the voiceover do the real talking. (Note: This doesn't apply to accessibility captions, which are essential).
- Illustrate, Don't Repeat: If your narrator says, "Click the 'Submit' button," show an animation of a cursor clicking that button. Don't also add the text "Click the 'Submit' button" right next to it. That's redundant.
The Spatial Contiguity Principle
What It Means: People learn better when words and the pictures they describe are placed close to each other. It’s that simple. If a label is way over on one side of the screen and the part of the diagram it's describing is on the other, the employee has to mentally connect the dots. That’s extra work.
Keeping text and its related visual right next to each other makes it effortless for the brain to see the connection.
How to Apply It in Mindstamp:
- Place Labels Directly on Images: Use Mindstamp’s text callouts or drawing tools to put labels right on top of the product part or diagram element you're explaining. No searching required.
- Integrate Questions with Content: When you add a question in Mindstamp, make sure it pops up immediately after the video segment it relates to. This tight connection reinforces the lesson and gives the employee instant context.
These four principles are all about streamlining the learning process. Here's a quick cheat sheet for putting them to work in Mindstamp.
Applying Principles for Reducing Cognitive Load
By mastering these simple but powerful ideas, you can transform your training videos from cluttered and confusing to clear and effective.
And remember, breaking longer training sessions into smaller, more focused chunks is another fantastic way to apply these concepts. For more on that, you can explore different microlearning strategies to make your corporate content even more powerful.
Structuring Complex Topics for Easy Learning
Once you’ve cleared the path by removing all the mental clutter, the next challenge is guiding your employees through the really dense stuff without overwhelming them. Some topics are just naturally complex, like multi-step technical processes or intricate compliance procedures. The goal isn’t to dumb down the material, but to structure it in a way that works with the brain's natural limits, not against them.
This is where the next batch of multimedia learning principles comes into play. These are all about managing complexity. Think of them as the architectural blueprints for building a solid foundation of understanding, ensuring even the most challenging corporate training can be broken down, digested, and actually remembered.
The Segmenting Principle
What It Means: People learn better when a big lesson is broken into smaller, bite-sized pieces. It’s like eating a huge meal—you wouldn't try to swallow it all in one bite. You cut it into manageable chunks. The same logic applies to corporate training.
A single 45-minute video on cybersecurity policies is intimidating and totally ineffective. But five separate 9-minute videos, each tackling a specific policy? That feels approachable and gives the employee a real sense of progress and control.
How to Apply It in Mindstamp:
- Create Chapters for Self-Paced Learning: Use Mindstamp’s chaptering feature to split a long video into distinct, labeled sections. This lets employees pause, reflect, and easily jump back to a part they need to review. For dense compliance training, this is an absolute game-changer.
- Build a Video Series: Instead of one monster video, create a playlist of shorter, focused videos. Not only is this easier to digest, but it also means you can update individual sections later without having to redo the entire training.
- Insert Pauses and Questions: Strategically place questions or other interactive elements in your video. These act as natural breaks, forcing the learner to stop and process what they’ve just seen before moving on.
The Pre-training Principle
What It Means: People learn more deeply when they already know the names and basic characteristics of the main concepts before the main training begins. It's like getting a glossary of key terms before reading a technical manual. It gives the employee a mental framework to hang all the new information on.
When employees don’t have to struggle with basic definitions, they can dedicate their full cognitive power to understanding how all the concepts actually work together. This is a must for any technical or specialized corporate training.
How to Apply It in Mindstamp:
- Create a Short Intro Video: Before diving into a complex process, make a brief (1-2 minute) intro video that just defines key terms and introduces the main components. Think of it as the "cast of characters" for your training video.
- Use Interactive Hotspots for Definitions: As you introduce new terms in your main video, use a hotspot that viewers can click. This can pop up a quick text definition or even a short video explanation without ever leaving the main content.
- Provide a Downloadable Guide: Add a button right in your Mindstamp video that lets employees download a one-page PDF with key concepts. They can keep it handy and refer to it throughout the training.
By front-loading the foundational knowledge, you clear the runway for a much smoother learning experience. Pre-training ensures that when the complex part of the lesson begins, your employees are prepared and confident—not confused and left behind.
The Modality Principle
What It Means: This is one of the most powerful principles out there. In short: people learn better from graphics and narration than from graphics and on-screen text. It's almost always better to say it than to display it as text in a training video.
Think about it. When you have a graphic on screen and a big block of text explaining it, your employee's eyes have to jump back and forth. This splits their visual attention and cranks up the cognitive load. But when you use a voiceover, the brain can process the visuals with the eyes and the audio with the ears simultaneously. It's a much more efficient, two-channel experience.
First introduced way back in 1989, the modality principle highlights a critical insight into how we process information. When visuals and text compete for the same channel (the eyes), it leads to overload. Narration neatly sidesteps this by using the auditory channel, freeing up the eyes to focus entirely on the graphics. You can dig into the cognitive science behind this in the original research on multimedia learning.
How to Apply It in Mindstamp:
- Narrate Your Demonstrations: When creating a product walkthrough or software demo, use a clear, concise voiceover to explain what's happening. This lets the employee focus 100% of their visual attention on your cursor movements and the interface.
- Keep On-Screen Text Minimal: Only use on-screen text for essential keywords, labels, or super short summary phrases. Absolutely avoid putting long sentences on the screen that your narrator is also reading aloud.
- Use Audio for Explanations: Got a complex chart or diagram? Use your voice to walk the employee through it, step-by-step. Don't crowd the visual with paragraphs of text trying to explain what each part means. Let your voice be the guide.
Driving Active Learning with Interactive Content
So far, we’ve focused on clearing away mental clutter and structuring complex topics. Now, it's time to shift gears. We're moving from making content easier to watch to making it impossible to ignore.
This is where passive viewing dies and active participation is born, turning your corporate training from a one-way lecture into a genuine two-way conversation.
Here, we'll dig into the Multimedia, Personalization, and Voice Principles and show you how to use them to foster deep engagement. Think of these principles as the engine behind active learning, turning your employees into participants who think, choose, and apply what they're learning in real time.
The Multimedia Principle
What It Is: This is the core idea that interactive video platforms like Mindstamp are built on. Simply put, people learn better from words and pictures together than from words alone. It's a foundational concept: combining what we see with what we hear leads to much deeper understanding.
When an employee can watch a process unfold while also hearing it explained, their brain forms stronger connections. This dual-coding approach makes the information stickier and way easier to recall later on the job.
How to Apply It in Mindstamp:
- Illustrate Every Concept: Don’t just talk about a new software feature; fire up a screen recording and show it in action. Make sure your narration is perfectly synced with visuals that support what you're saying.
- Use Images and Diagrams: Add diagrams, charts, or even simple images to make abstract concepts tangible. A quick flowchart, for example, can make a complex workflow instantly click for someone.
- Embed Interactive Elements: Platforms like Mindstamp exist to bring this very principle to life. You can learn exactly how to create interactive videos that put this concept into practice.
The Personalization Principle
What It Is: People learn better when the tone is conversational and friendly, not formal and stuffy. Using words like "you" and "your" makes the employee feel like they're in a one-on-one coaching session instead of a generic corporate lecture.
It's a small change, but it completely lowers their defenses and boosts engagement. It sends a clear signal to the employee that the content is made specifically for them, making them far more receptive to the material.
A personalized approach transforms a generic corporate video into a supportive, human experience. When employees feel like you're speaking directly to them, they're much more motivated to pay attention and participate.
How to Apply It in Mindstamp:
Let's say you're creating a training video on new customer service protocols. Here’s how you can apply the Personalization Principle in your script and questions.
Before (Formal):
- Narration: "Employees must follow the three-step de-escalation process."
- Question: "Which step of the process is most critical?"
After (Personalized):
- Narration: "When you encounter a frustrated customer, your first step is to listen. Let's walk through how you can do this effectively."
- Question: "Based on what you just learned, what would you say to a customer in this situation?"
That simple shift from "employees" to "you" makes all the difference. For those looking to build even more sophisticated interactive experiences, exploring effective strategies for mobile app development can offer some great parallel insights.
The Voice Principle
What It Is: This one feels obvious once you hear it: people learn better from a friendly human voice than a machine-like, robotic one. A warm, enthusiastic voice conveys personality and care, which helps build an actual connection with the employee.
A flat, computer-generated voice can be incredibly distracting and immediately signals that the training is low-effort. A real human voice, on the other hand, sounds more trustworthy and engaging, making it much easier for employees to stay locked in.
How to Apply It in Mindstamp:
- Record with a Good Microphone: You don't need a professional studio, but a decent USB mic can make a world of difference. Clear, crisp audio is non-negotiable for keeping your audience's focus.
- Speak Naturally: Record your script like you're explaining something to a colleague over coffee. Let your natural passion for the topic shine through in your tone.
- Choose a Voice That Fits: Find a narrator whose voice aligns with your company's culture. Whether it’s upbeat and energetic or calm and reassuring, the right voice can set the perfect learning atmosphere.
Building an Interactive Onboarding Video Step-by-Step
Theory is great, but seeing the multimedia learning principles in action is where the magic really happens for corporate training. We're going to move from ideas on a page to a concrete, practical blueprint you can use right away.
Let’s walk through creating an interactive onboarding video for a new sales hire. The goal? Get them up to speed on your company's Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software. This isn't just a one-off example; it's a model you can tweak for almost any training topic. We’ll use Mindstamp’s features to turn a basic screen recording into something truly effective.
Step 1: Script and Record with a Human Touch
Before you even think about hitting record, it all starts with the script. For our CRM training, we want to teach three core functions: creating a new lead, logging a call, and updating an opportunity.
First up, the Personalization Principle. Write your script like you're talking to a new team member, not an anonymous user. It's a simple change that makes a world of difference.
- Instead of: "The user must first click the 'New Lead' button."
- Try: "To get started, you’ll click the 'New Lead' button in the top right corner."
Next, think about the Modality Principle. Your script should be what you say, not what you put on the screen. This frees up your new hire to actually watch what you're doing in the CRM. They can focus their eyes on the interface while your voice guides them, instead of trying to read and watch at the same time. Keep the language simple and skip the jargon.
Step 2: Structure the Video for Focus, Not Frustration
Nobody wants to sit through a long, rambling screen recording. It’s a fast track to cognitive overload. So, let's build a smarter structure from the get-go using the Segmenting Principle.
Once your recording is done, upload it to Mindstamp. The very first thing you’ll do is chop it into logical pieces.
- Create Chapters: Use Mindstamp’s chaptering feature to create three clear sections: "Creating a New Lead," "Logging a Call," and "Updating an Opportunity." This gives your new hire a roadmap and lets them control the pace.
- Add a Pre-training Intro: Right at the start, pop in a quick text overlay or a short intro clip. Use it to define key CRM terms they’ll hear, like 'Lead,' 'Opportunity,' and 'Pipeline Stage.' This is the Pre-training Principle in action, giving them the foundation they need before the real lesson begins.
Step 3: Add Interactive Layers to Guide and Engage
Okay, now for the fun part. This is where we layer in the interactive elements that shift the experience from passive viewing to active learning, bringing the Signaling and Multimedia Principles to life.
Throughout the video, you’ll drop in specific interactions:
- Use Hotspots to Signal: When your voiceover says, "...click the 'Save' button," add a Mindstamp hotspot that puts a pulsing circle right around that button on the screen. This eliminates any guesswork for the new employee.
- Insert Questions to Check for Understanding: After the "Logging a Call" chapter, add a multiple-choice question: "What's the most important field you need to fill out after a client call?" This not only reinforces the lesson but gives them instant feedback.
See how this works? Multimedia learning principles aren't just academic fluff. They're practical design choices. Each feature—chapters, hotspots, questions—is there for a specific cognitive reason, helping the brain learn more effectively.
Step 4: Finalize and Share Your Interactive Training
With the structure and interactions locked in, you're almost there. The final step is a quick review. Put yourself in the shoes of a brand-new employee watching this for the first time. Is the narration clear? Do the hotspots pop up at just the right moment? Do the questions make sense?
By following this blueprint, you've created way more than just a training video. You’ve built an interactive learning experience that works with the brain's natural learning process, not against it. You’re guiding their attention, involving them directly, and ultimately, creating a tool that gets new hires up to speed faster and helps them perform better from day one.
Answering Your Questions About Multimedia Learning

Knowing the theory behind multimedia learning principles is one thing, but actually using them in the real world of corporate training is a whole different ball game. We’ve all been there—juggling tight deadlines, rigid brand standards, and a mountain of existing content.
Let's dive into some of the most common questions that training managers ask when putting these powerful principles into practice. The goal here is to give you direct, actionable answers so you can confidently create training that truly works.
How Do I Balance These Principles with Strict Brand Guidelines?
Ah, the classic dilemma. Your brand guidelines might insist on a certain font, a corporate color overlay, or background music in every single video—all things that can butt heads with principles like Coherence or Signaling.
The key here is negotiation and education. Instead of just saying "no" to the marketing team, explain the "why" behind your request. Show them how a cleaner, distraction-free video leads to better learning, which in turn boosts employee performance. That’s a metric everyone can get behind.
Pro-Tip: Try proposing a "training video variant" of the brand guidelines. This could mean allowing for simpler graphics or ditching the background music for educational content. You preserve the brand’s integrity while making learning the top priority.
Often, you can find a happy medium. For example, you could use brand colors for key highlights (Signaling) rather than a full-screen wash. Or maybe the corporate jingle plays only at the very start and end, leaving the core teaching segments clear and focused.
Is On-Screen Text Ever Better Than Narration?
While the Modality Principle generally says to favor narration over blocks of on-screen text, there are a few important exceptions in a corporate setting. In some cases, text isn't just better; it's essential.
- Technical Terms and Acronyms: When you introduce a complex term or a new company acronym (like "QBR" for Quarterly Business Review), putting it on the screen helps with spelling and locks it into memory.
- Key Takeaways or Steps: A simple text overlay that summarizes a three-step process gives employees a clear visual anchor they can easily refer back to.
- Accessibility: This one’s non-negotiable. For employees who are deaf or hard of hearing, or for anyone in a loud office without headphones, accurate captions are an absolute must.
The rule of thumb is to use text to support the narration, not just repeat it. Avoid putting long, word-for-word sentences on the screen that the narrator is already reading aloud.
What Is the Best Way to Start Applying These Principles?
Staring at a huge library of existing training videos can feel overwhelming. Don't sweat it—you don't have to overhaul everything at once. The best way to get started is to think small and prioritize.
- Pick One High-Impact Video: Start with a training video that’s critical for new hires or is tied to a major business goal, like compliance or a new software rollout. Making even one important video better will deliver the biggest bang for your buck.
- Focus on "Subtraction" First: The easiest win is applying the Coherence Principle. Go through your chosen video and just start removing things. Cut the distracting background music, delete irrelevant stock photos, and trim down wordy explanations.
- Add Simple Signals: Once you've cleaned house, layer in some basic Signaling. Using a tool like Mindstamp, you can easily add a few hotspots or text callouts to draw attention to the most critical pieces of information.
By starting with a single video and making these targeted tweaks, you can build momentum and show stakeholders the real-world value of these principles—all without kicking off a massive, time-consuming project.
Ready to turn theory into practice? With Mindstamp, you can easily apply chapters, add hotspots, and insert questions to transform your passive corporate training videos into active, engaging learning experiences. See how it works and start building more effective training today at https://mindstamp.com.
Get Started Now
Mindstamp is easy to use, incredibly capable, and supported by an amazing team. Join us!


Try Mindstamp Free










